lecture on jj gibson's contribution 30 march 2016
The Light which comes from the several points of the Object is so refracted as to ... paint the Picture of the object upon that skin called the Retina.

what is a picture exactly?

A picture is a surface so treated that it delivers an angular optic array to a point of observation in front of it that contains some of the information in a sector of the original optic array at the point of observation. Photograph.

But a picture can also provide an eye with a different pattern of stimulus energies and the same stimulus information that the original array provided. Cariacature.
Point-projection is a powerful theory.
Point-projection includes the theory of the projected retinal image.

Light is, in fact, projective; one can project shadows or transparent pictures and the abstract notion of point-to-point correspondence is part of the branch of mathematics called projective geometry.

Projective Geometry is an elementary, non-metrical geometry.
e.g. it is not based on a concept of distance.
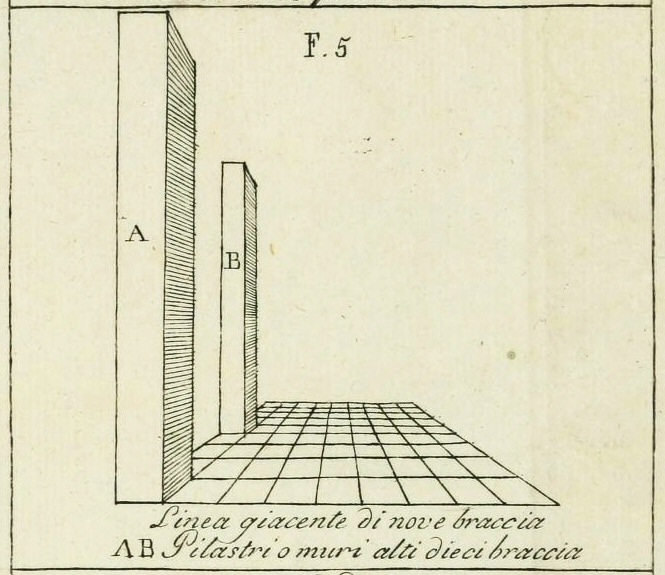
consider graphical perspective, a subset of projective geometry.
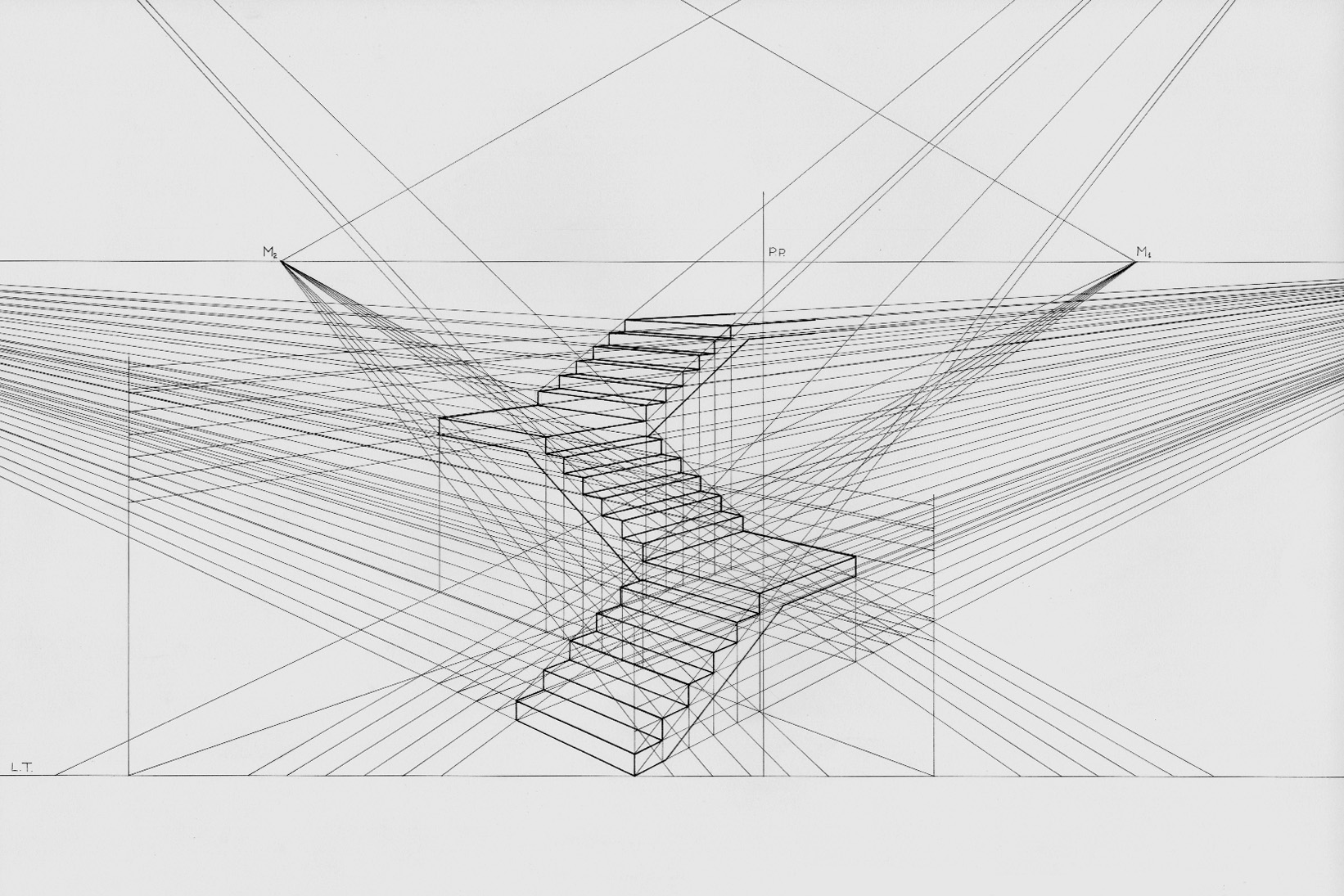

perspective: rule 1
the image of a straight line is a straight line
perspective: rule 2
images of parallel lines are coincident
The two most characteristic features of perspective are that objects are smaller as their distance from the observer increases; and that they are subject to foreshortening, meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight are shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight.
single-point perspective

two-point perspective

let's assume that the fidelity of a picture is analogous to the fidelity of a sound recording.
but how are the two analogous? what is analogous?
A faithful picture yields a sheaf of light-rays to a given point which is the same as would be the sheaf of rays from the original scene to a given point, that is, when the adjacent order of the points of color in the cross-section of one corresponded to the adjacent order in the cross-section of the other and when the forms in the one cross-section are congruent with the forms in the other.
this faithful picture resembles a perspective system for light rays.
Good measure of fidelity of a photograph, useless for the caricature.
THE SYMBOL THEORY OF PICTORIAL INFORMATION
a picture may be composed of symbols and one may learn to read a picture as the child learns to read English.
critique from Nelson Goodman
In diametric contradiction to what Gibson says, the artist who wants to produce a spatial representation that the present-day Western eye will accept as faithful must defy the "laws of geometry."

If a picture is neither the source of a sheaf of different light rays each corresponding to a spot on the surface nor a layout of graphic symbols like writing, on the other, what is it?
A NEW THEORY OF PICTORIAL INFORMATION
A picture is a surface so treated that a delimited optic array to a point. Of observation is made available that contains the same kind of information that is found in the ambient optic arrays of an ordinary environment.
the same kind of information
what information?
Information consists of invariants, in the mathematical sense, of the structure of an optic array.
invariant 1
the upper hemisphere of the optical array (the sky) tends to be much less structured and brighter than the lower hemisphere (Earth).
invariant 2
objects grow or shrink as an observer moves towards or away from them.
invariant 3
close objects occlude faraway objects.
Gibson hypothesized that agents evolved to directly access relevant information about themselves and the environment from the invariant structures in the array, without the need for high level cognitive computation.
These invariant properties are linked with Gibson’s idea of affordances.

So, when you see an object you don't see its surface in perspective. You see all of it the back as well as the front. All of its aspects are present in the experience.
so, how would you design photographs to make incorrect assumptions about the